Strategy
The master lines of the strategy for the future are based on three pillars:
ecological sustainability initiatives.

economic and social development based on digitization.

The Company’s strategy integrates the major areas of sustainability to face the mission “to make our world more human, connecting people’s lives” and the Responsible Business Principles, which incorporate the code of ethics and policy of responsibility towards stakeholders with the commitment to achieve efficiency, growth and long-term value with the trust of all (stakeholders).
(GRI Contenido 203-2)
Leading by example and building trust across the activity.

Sustainability is found both in what to do as well as how to do it. The “what to do” guarantees economic results, but the “how to do” ensures that such results are obtained based on good business management from a social and environmental perspective. In this sense, for the Company, sustainability is not an additional issue to the core, but rather ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) management is cross-cutting and is immersed in the business strategy.
Although since the beginning of the Company’s operations in Colombia, it has been focused not only on generating economic value, but also that this is achieved with responsible business conduct, thus in the year 2021, it entered into the legal status of a Benefit and Collective Interest Company (BIC). Now, the Company’s corporate purpose includes eight activities within the framework of five dimensions: Business model, Corporate governance, Labor practices,
Environmental practices and Community practices (see chapter 6).
Within this framework, Movistar, as a key player in the Information and Communications Technology (ICT) sector, has taken responsibility for its impact on the environment and has committed to fulfilling the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Although Goal 9 (building resilient infrastructures, promoting sustainable industrialization and fostering innovation) is the main goal in which the Company generates value, there are other goals in which it generates impact, in particularly those SDGs related to economic growth and equal opportunities (SDG 5, SDG 8 and SDG 10), environmental protection (SDG 7, SDG 12 and SDG 13), quality education (SDG 4), development of sustainable societies (SDG 11), ethical behavior and integrity (SDG 16) and partnership building (SDG 17) (see chapter 5.5).
Risk Management Model
The Company conducts ongoing monitoring of the most significant risks that could affect the achievement of its goals. To do this, and as part of the Telefónica Group, it has a risk management model based on COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations, of the Treadway Commission), itself is uniformly implemented in the primary operations of the Telefonica Group and the Company’s responsible staff, within their scope of action, performs the appropriate identification, evaluation, response and tracking of the principal risks.
This model, inspired by best practices, facilitates the prioritization and development of coordinated actions against risks, both from a global perspective of the Telefónica Group and specifically in its main operations.
Risk management provides added value to the organization by selecting and implementing specific responses to reduce risk, and where appropriate, transferring them to a third party or accepting them. The Risk Management Model defined by the Telefónica Group provides a high degree of risk awareness and ensures a more efficient allocation of resources to manage identified risks.
The Telefónica Group’s Responsible Business Principles specifically state that: “We establish adequate controls to assess and manage all relevant risks to the Company” Extract from Telefónica’s Responsible Business Principles. In this regard, the Company has a Risk Management Policy, approved by the Board of Directors, and a Corporate Risk Management Manual of the Telefónica Group, both based on experience, best practices and Good Corporate Governance recommendations, thus contributing to continuous improvement in the performance of the business.
As a result of the Risk Management process, the company prioritizes the main incidents through a Risk Map considering the following categories:
Business: from a business standpoint, these are risks derived from the economic and political environment, regulatory changes, as well as the entry of new competitors, in addition to innovation and other incidents that may affect the Company’s sustainability and reputation.
Operational: from the operational management point of view, these are the risk incidents derived from failures in the network, IT systems, security, quality of customer service, cyberattacks, among others.
Financial: these are risks derived from adverse activity in the economic environment or financial variables such as exchange rates or interest rates, as well as tax risks and Commercial Credit risks.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: risks related to litigation of different nature or related to the compliance of obligations by the Company that may affect not only in economic terms but also the Company’s image and reputation.
The risk management process uses the Company’s
strategy and objectives as a reference to
identify the main risks that could affect said
objectives. It includes an assessment from two
complementary perspectives: top-down and
bottom-up, which as well as identifying and
describing the specific operational risks,
proposes an analysis of the issues considered
critical and common to the companies of the
Group.
Similarly, the model includes the identification
of issues that, despite their results and
temporary horizon being uncertain and difficult
to predict, could have a potential adverse
impact on the Company’s future performance.
Once identified, the risks are assessed
according to the combination of impact, whether
qualitative or quantitative, and the probability
of occurrence, considering additional factors,
such as the historical trend of the risk and the
period of time in which the risk incident could
materialize, enables the prioritization of
monitoring and response to the risks, whether
through mitigation plans to minimize their
impact or with actions to prevent or transfer
said risks.

The Risk Management Model periodically analyzes the internal and external context of the Company looking for information:

¿What’s going on around the world? trends, circumstances and/or external, political, economic, cultural and other situations that benefit or affect us. Some references are the World Economic Forum, Gartner, Ernest & Young, KPMG, Deloitte, among others.
¿What do Telecom or Technology companies say? risks or opportunities that our competitors or Partners such as Google, Microsoft, Netflix, AT&T, among others, where we can cross-identify what they or we can identify in terms of risks.
¿What do other operators view? recognize whether the risks or opportunities that operators in other countries have may affect us, for example, Hispam and Big 42, looking to identify common issues or others that are gaining relevance in a given country.
¿What is visible inside and what do customers, suppliers, partners, employees and others think about it? internal situations that can be used to turn them into opportunities or that must be controlled because they are a potential risk. As well as getting to know the related needs and expectations of the interested parties becomes a duty to work or a regulatory requirement to comply with.
2Big 4 refers to the Telefónica Group’s focus on four
key operators: Spain,
Germany, the United Kingdom and Brazil.
Both the Responsible Business Principles and the previously mentioned Risk Management Policy establish that the entire organization is responsible for contributing to the identification and management of risks. In order to coordinate these activities, the following roles are established:
Supervision of Risk Management
The Board of Directors, through its Audit Committee, is the entity’s body that supervises the process. Similarly, the Board of Directors examines the risks presented by the Risk Management function from both the perspective of risks common to the Group and of risks specific to operation.
Risk responsibility
The people responsible for the risks or risk owners actively participate in the risk strategy and in the important decisions on their management, preparing a plan for their mitigation and conducting effective monitoring of their evolution.
Risk Management Function
A function independent from management within the Internal Auditing department in charge of driving, supporting, coordinating and verifying the application of the Policy, supporting the Audit Committee and Steering Committee in the amount of matters required.
The Company faces a variety of risks during the course of its activities arising from external or internal factors, in some cases incidents specific to the Organization, risks related to the telecommunications sector or events related to the political or economic environment of the country. The most significant risks and uncertainties faced by the Company that could affect its business, financial position, and results, should be considered together with the information included in the financial statements:
- Rising inflation rate, which increases operating costs. The global context has become more challenging, high inflation and rising interest rates in developed countries have led to a weakening of external demand, lower commodity prices and a tightening of global financial conditions, which represents a downside risk for economic activity in 4Q22 and 2023.
- Fluctuations in interest rates, both local and foreign, affect the cost of funding the operation and the return on surpluses invested in financial assets. It affects the financial result and impacts cash flow.
- The Company’s financial condition and results of operations could be affected if exposure to foreign currency exchange rates is not effectively managed.
- Regulatory conditions of entry to wholesale services, such as call termination and interconnection, can significantly affect the competitive scenario faced by the company, the reference prices in the market and, therefore, the profitability of the services.
- The management of the supply chain entails labor risks, mainly due to obligations arising from the subsidiary responsibility and collective action against third parties in the case of outsourced activities, as well as the need to manage motivation and quality of the services provided by third parties on behalf of the Company.
- Information technology is a relevant element of the business and is exposed to cybersecurity risks. Despite progress in modernizing the network, and replacing aging systems pending of technological renewal, the Company operates in an environment of increasing cyber threats and all of its products and services are inherently dependent on information technology systems and platforms that are susceptible to cyber-attack. Successful cyber-attacks can obstruct the effective marketing of products and services to customers, the possible leakage of information or unauthorized access, so it is necessary to further advance in the identification of technical vulnerabilities and security weaknesses in operational processes, as well as in the ability to detect and react to incidents.
- Eventual system failures may result in loss of quality or interruption of service: events related to extreme natural disasters could affect the availability of information systems that support the Company’s critical services.
- The Company is involved in litigation of different nature.

Stakeholder engagement
(GRI Content 2-29)
The Company is interested in building trusting relationships with its stakeholders. According to the stakeholder mapping conducted to launch the Stakeholder Panel consultation, the following seven key stakeholder groups have been defined:

Stakeholder engagement allows the Company to understand the context in which it operates, as well as identifying both strengths and opportunities for improvement to define its action plans.

In addition to the Stakeholder Panel and with the aim to maintain an ongoing dialog, the Company carries out stakeholder engagement through other tools and channels to find out their opinion:
Shareholders and Investors
The Company has both a Shareholder Service Office and an Investor Service Office. In 2022, in addition to the General Shareholders’ Meeting, was held a conversation with shareholders in which it reported on the Company’s impact management: year-end and mid-term financial statements and corporate social responsibility. Likewise, in the case of investors, it was received 35 requests from 23 investors, giving responses by mail or scheduled meetings.

Customers
In general, customers seek solutions in each of the contacts they have with the Company, hopefully in the first contact without requiring referral to other areas that the customer contacts. The processes that are most commented by customers are on the operation and technical support, self-managed service and supply front. On these topics and others, the Company conducts in-depth research to understand the customer’s perception and to be able to incorporate the voice of the customer in the design of the Company’s products, services and experience.
These studies are designed by the quality team and managed under different procedures: telephone and digital surveys, Focus Group, mystery Shopper, call monitoring, Speech Analytics, in-depth interviews. In 2022, we conducted 78 in-depth studies, 45,000 surveys and more than 3,5 million individual process surveys.
The conclusions of these analyses are input for the development of action plans to improve the customer experience.
Transactional satisfaction surveys: Following each service or process performed by customers, it is sent a survey by SMS or email, in order for them to give feedback on their experience, rating their recommendations and satisfaction, within other categories. This survey is sent up to 48 hours after the service or completion of the process.
These surveys are conducted daily and the results are reported daily in order to execute action plans and react in a timely manner.
During 2022, a total of 3,808,230 surveys were conducted for a monthly average of 317,350 surveys.

Collaborators
The Motivation Survey is conducted annually which allows for the calculation of the eNPS (Employee Net Promoter Score) in order to know what is being done well and to reinforce it, as well as to identify areas for improvement. In 2022, the Company raised two percentage points from 80 to 82.
With collaborators were also performed:
- 8 coffees or face-to-face and virtual talks, led by the CEO, Directors and Regional Managers.
- 11 on-site visits by the CEO to the national locations.
- 5 large-scale Company quarterly meetings (1 Strategic Plan kick-off and 4 quarterly follow-up events). To ensure employee engagement, we developed in-person and hybrid formats through live broadcasts on the corporate social network Workplace. This social network allows us to have a permanent conversations with employees.

Journalists
During 2022, the Company mobilized 92 press releases and more than 120 interviews, and resumed face-to-face events with the media, with excellent reception, including 14 events to display the deployment of Fiber Optics in all regions of the country.
With the aim of having a much closer contact with journalists, 5 training and education spaces were generated, bringing new concepts on eSports, cybersecurity, Internet of Things, technology for the countryside, among others.
We also strengthened and enhanced the relationship with journalists through the promotion of new spaces such as WhatsApp Business.
In addition, the company opened scenarios for dialogue and training, such as #EspaciosMovistar, through the Movistar Press Twitter, eSports training and the first ABC Movistar: a space for dialogue about topics of interest and current affairs to generate a new dynamic for learning and collective interaction with journalists.
Through WhatsApp Business, we generated 460 conversations, attended more than 140 requests (VIP cases, management of spokespersons and interviews, advertising requests, etc.), and almost 90 contents were generated and shared (press releases, stories, engagement messages, etc.). Meanwhile, throughout the #EspaciosMovistar we had more than 600 listeners (including the general public of the @ptelefonicacol account) and the training sessions (eSports and ABC) were attended by nearly 100 people.
It is worth mentioning that diversity and inclusion issues are becoming more relevant day by day, which is how interest was created in the media and the general public with the Women in Network program.
For the Company, it is also significant to have day-to-day conversations in the media, social networks, unions, control entities, competition, and legislative agenda. For this reason, daily monitoring is performed to analyze risks and opportunities for the definition of action plans.
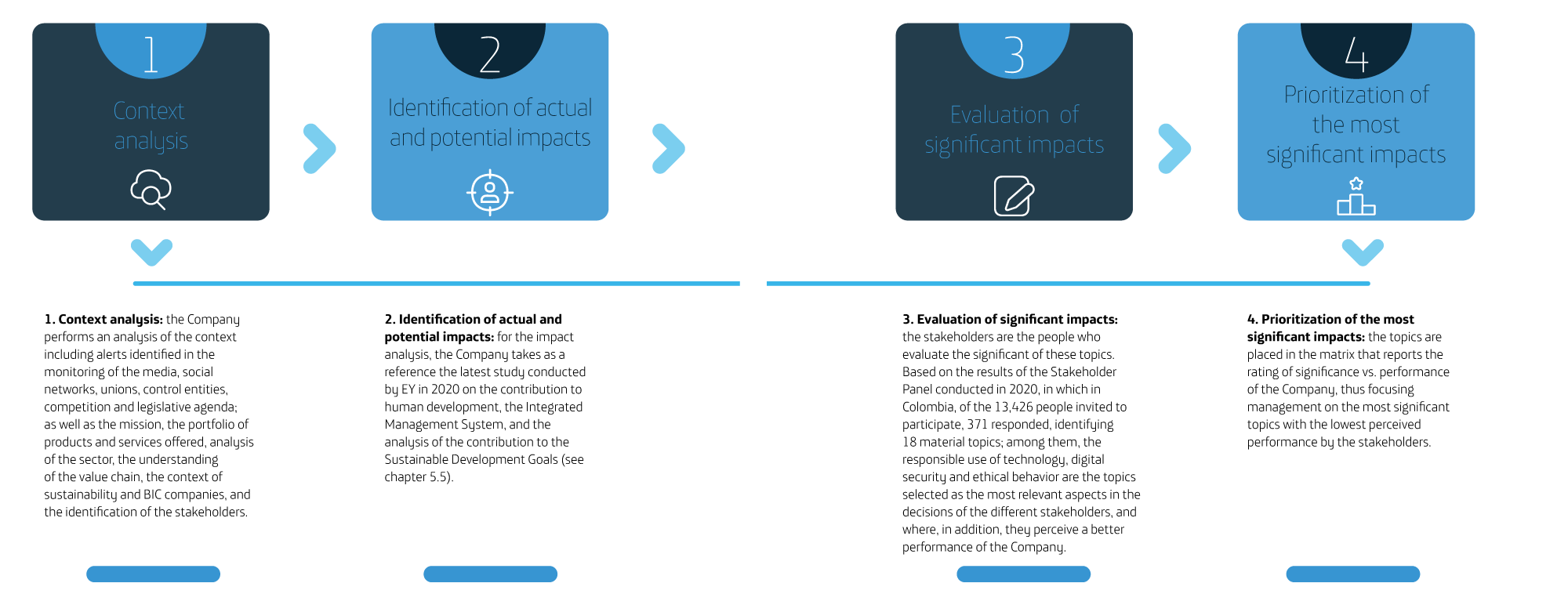
Materiality
(GRI Content 3-1)
To update the Company’s material topics, it considers the GRI Standards recommendations, following these four steps:
Interest group
Shareholders
Dialogue channel
- Stakeholder Panel
- General Shareholders’ Meeting
- Shareholder Service Office
- Responsible Business Channel
Material topics
Digital security, ethical behavior, and responsible use are the most relevant areas in their decisions and where they perceive a better performance of Telefónica.
Interest group
Investors
Dialogue channel
- Stakeholder Panel
-
Investor Service Office
- Responsible Business Channel
Material topics
Digital security, ethical behavior, and responsible use are the most relevant areas in their decisions and where they perceive a better performance of Telefónica.

Interest group
Government Entities and Regulators
Dialogue channel
- Stakeholder Panel
- Institutional meetings
- Responsible Business Channel
Material topics
Digital security and customer experience are key.
Interest group
Employees
Dialogue channel
- Stakeholder Panel
-
Responsible Business Channel
- eNPS
- Dialogues/ Coffee
- Diverse collaborators
- Workplace
- Intranet
-
Primary Committees
- Working Environment Committee
- Diversity Committee
- Occupational Safety And Health Committee (OSHC)
Material topics
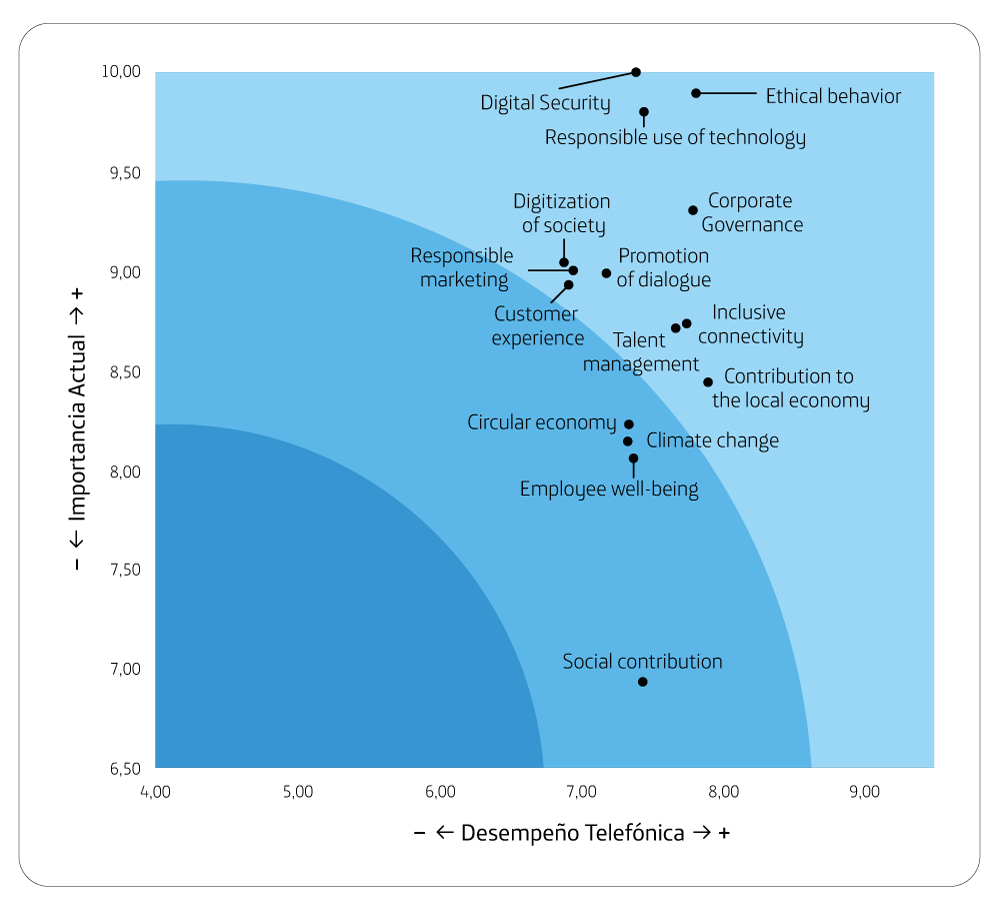
Ethical behavior, corporate governance and promotion of dialogue are the most relevant areas in their decisions and where they perceive a better performance of the Company.
Customer Experience and Talent Management are
the worst performers.
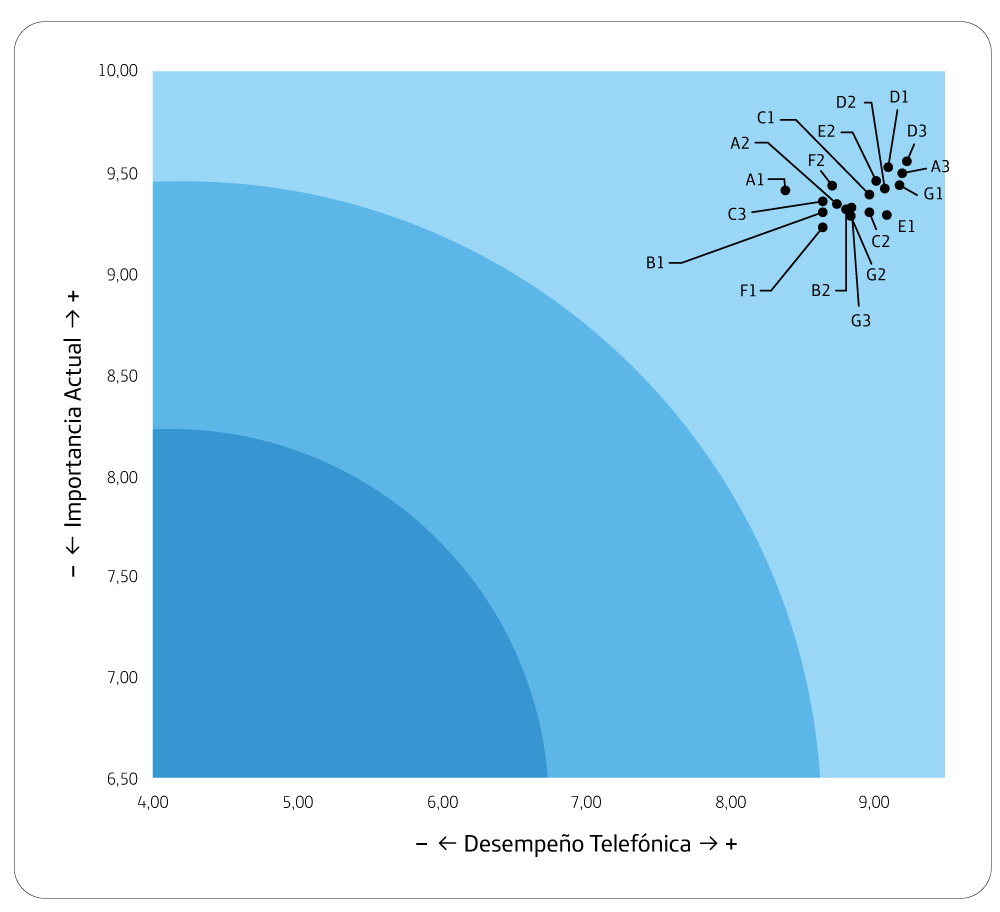
Interest group
Senior Management
Dialogue channel
- Stakeholder Panel
- Responsible Business Channel
- eNPS
- Dialogues/ Coffee
- Workplace
- Primary Committees
Temas materiales
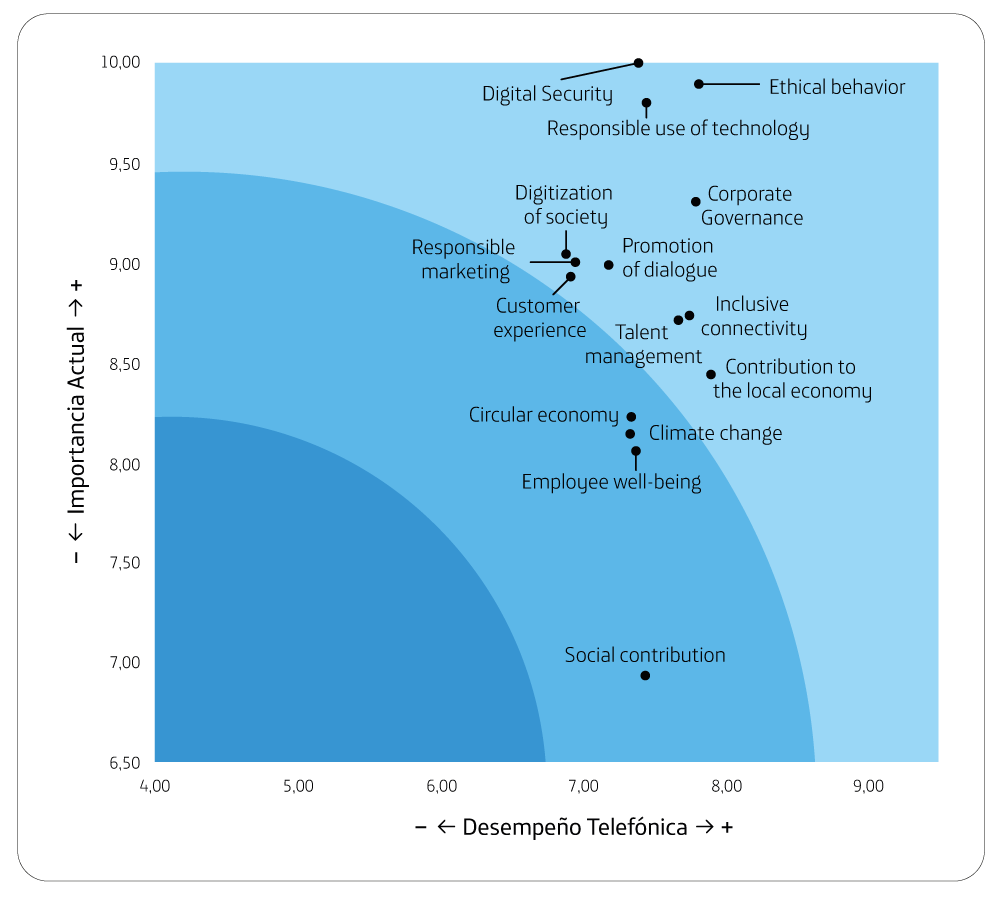
All the topics evaluated report a significant performance and relevance. Digital security, Responsible use of technology and Customer experience are the most important topics.
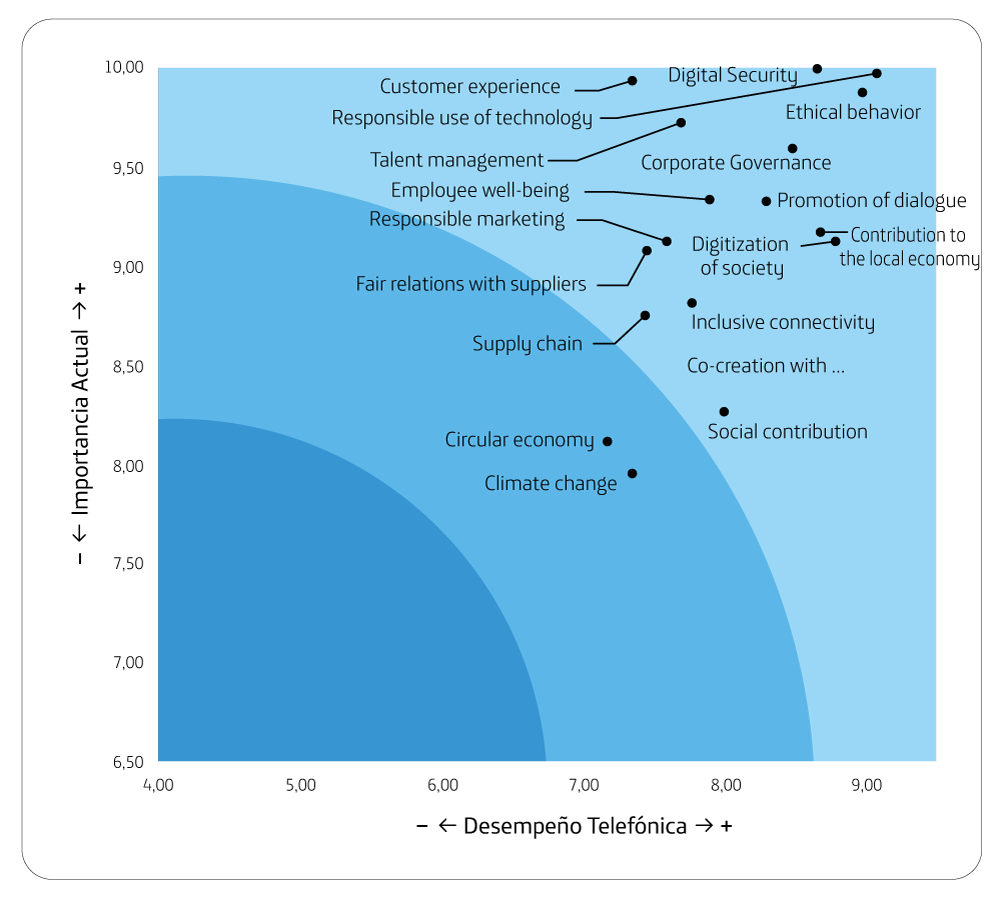
Interest group
B2B Customers
Canal de diálogo
- Panel de skateholders
- Canales de atención
- Canal de Negocio Responsable
- Redes Sociales
- Canales Preguntas, Quejas y Reclamos (PQR)
- Índice Satisfacción Clientes (ISC)
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Material topics
All topics show a remarkable performance. Issues related to business Ethics and corporate Governance are the most relevant in their decisions.

Interest group
B2C Customers
Dialogue channel
- Stakeholder Panel
- Service channels
- Responsible Business Channel
- Social networks
- Petitions, Complaints and Claims (PCC) Channels
- Customer Satisfaction Index (CSI)
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Material topics
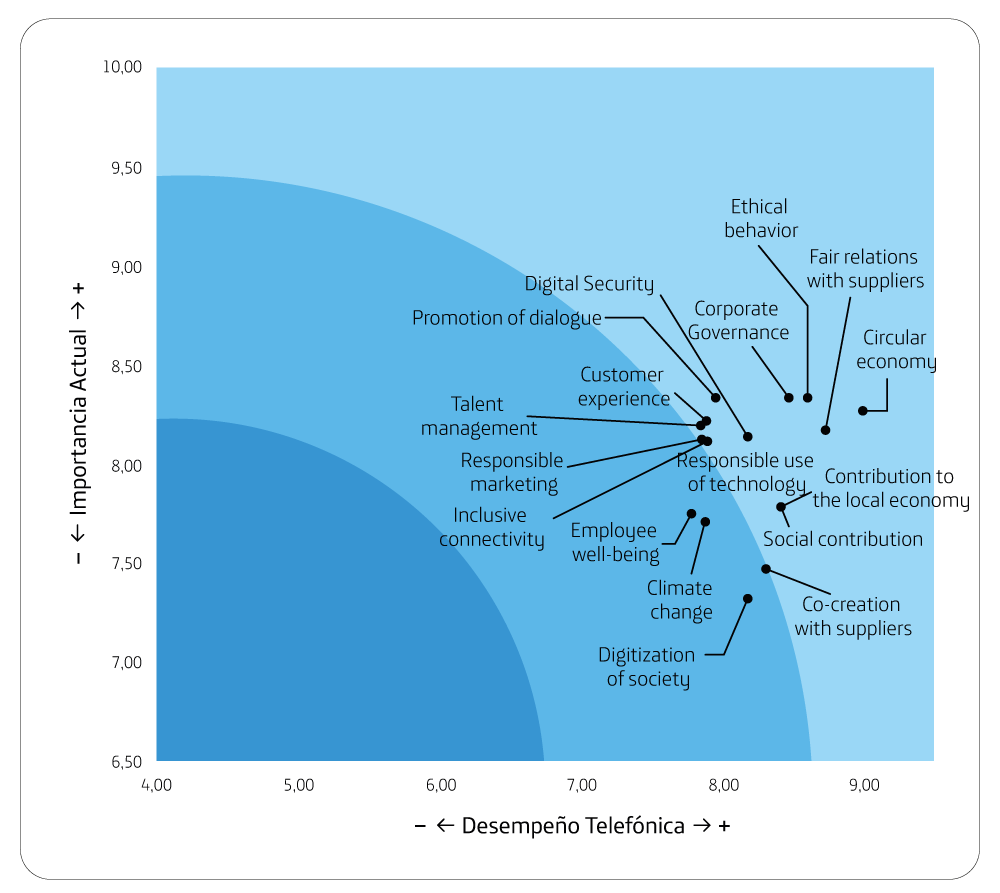
Responsible use of technology, Corporate Governance and Ethical behavior are the most relevant aspects in their decisions.
Custoer Experience and Responsible Marketing
Talent Management are the worst
performers.
Interest group
Suppliers
Dialogue channel
- Stakeholder Panel
-
Partners Channel
- Workshop
- Responsible Business Channel
-
E-Commerce Platform – Adquira and
GEP SMART
- Intranet and Customer Service Center – CSC
Material topics
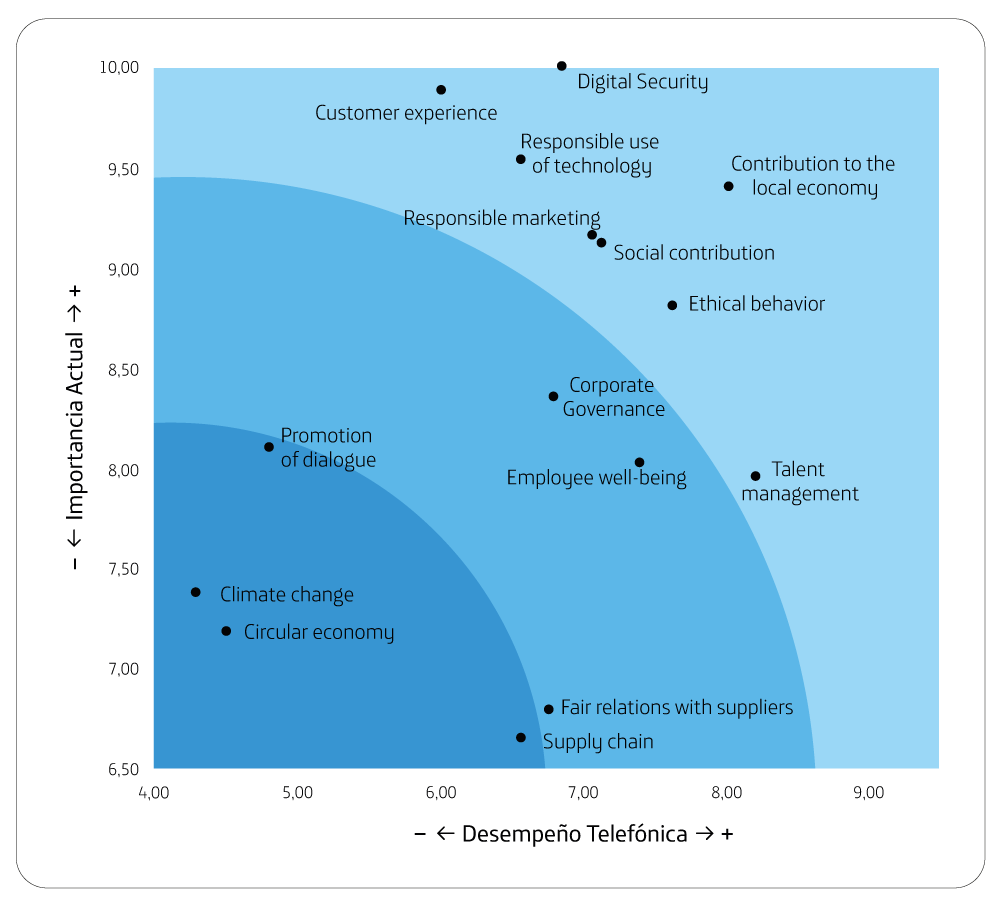
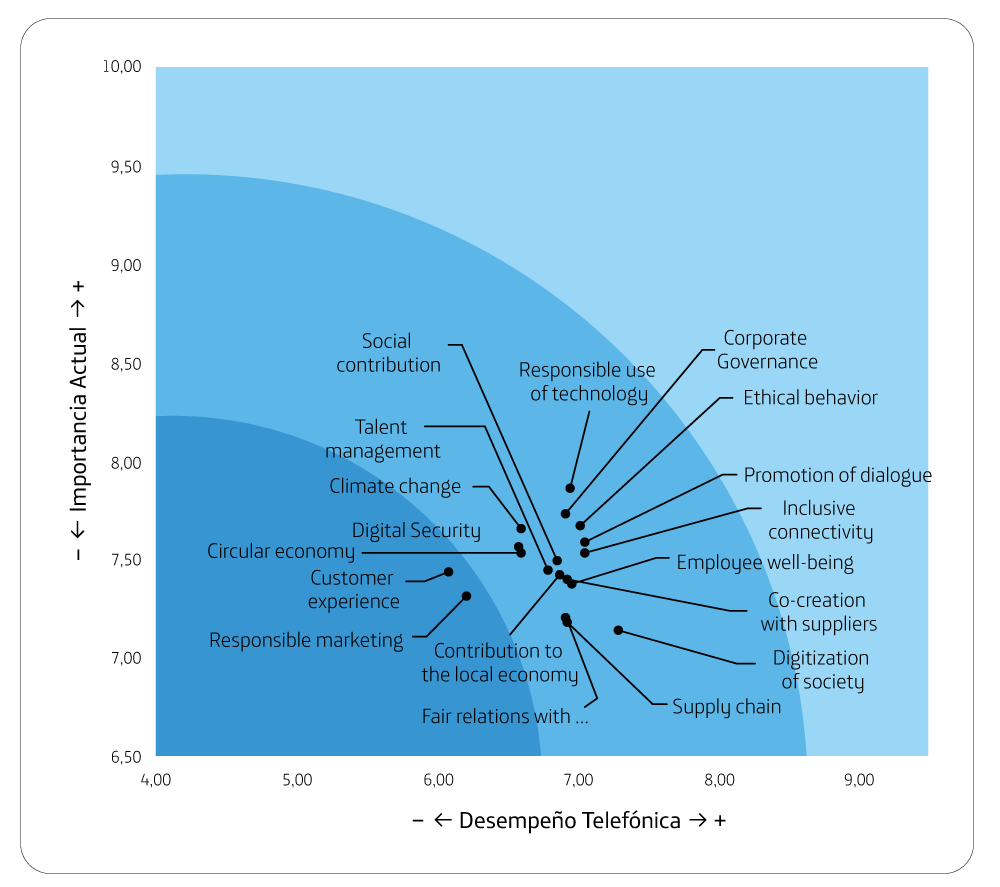
Ethical behavior, Fair relationship with suppliers and Customer experience are the most relevant topics in their decisions.
Fair relationship with suppliers, Customer
experience and Talent management are the worst
performers.

Interest group
Society
Dialogue channel
- Stakeholder Panel
- Reputation pulse
- Responsible Business Channel
-
Complaints and Claims Mechanism for Human Rights,
Institutional Relations and the Environment
Temas materiales
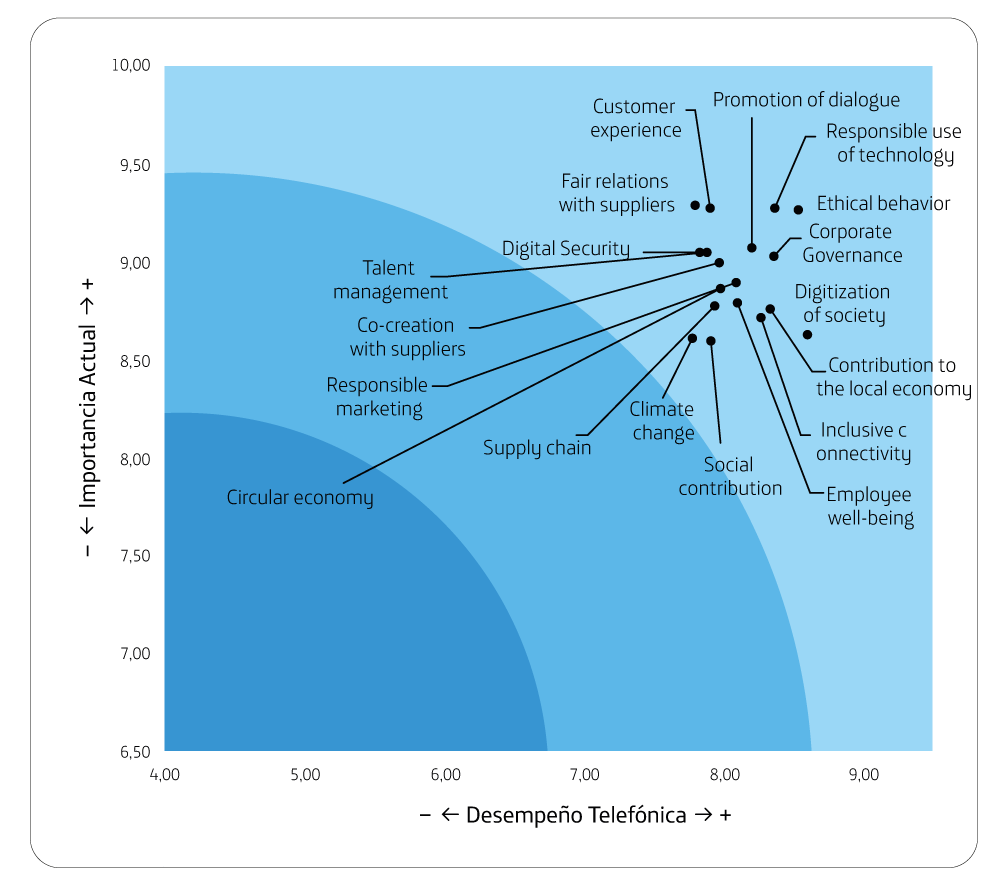
It is one of the groups in which the importance of all the topics are average, highlighting the responsible use of technology (8.87) and management with suppliers (8.67).
The best perceived is the Promotion of Dialogue (7.78), which is the attribute with the lowest importance for this group (7.64).

Interest group
Opinion leaders, media, and communication services
Canal de diálogo
- Stakeholder Panel
- Responsible Business Channel
- Press Conferences
- Visit to media
Temas materiales
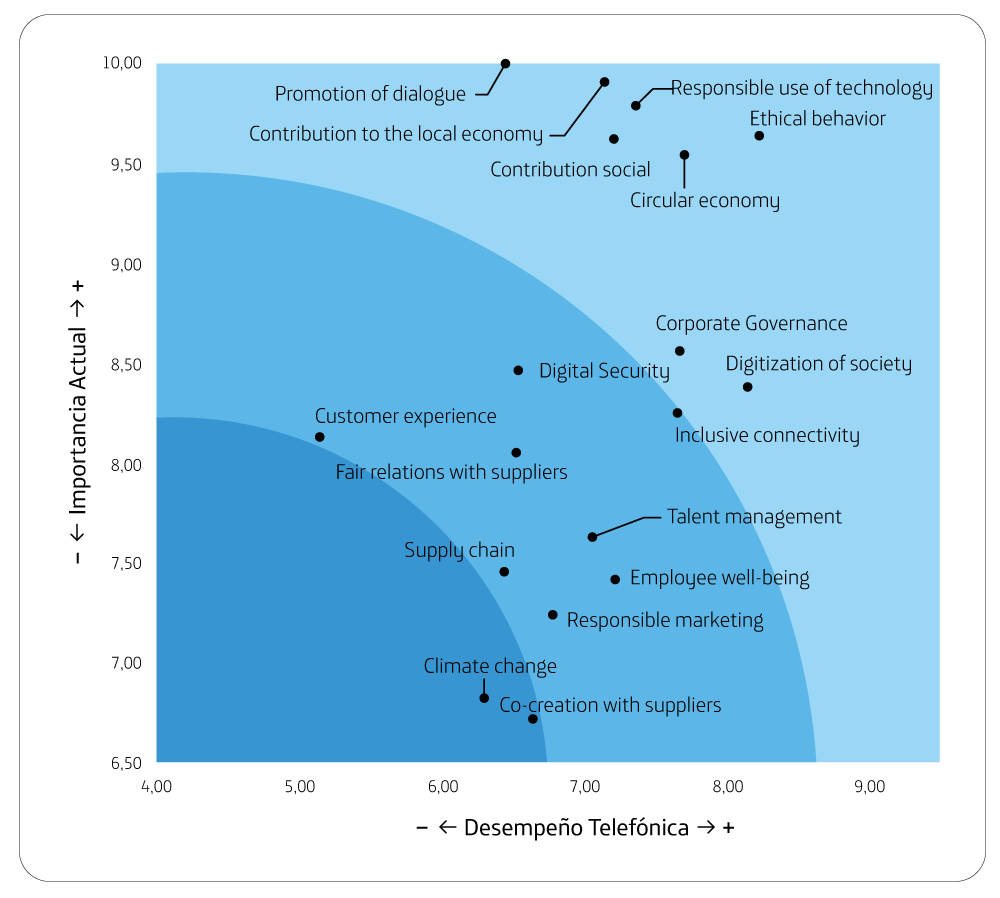
The matrix shows 3 zones differentiated by level of importance, promoting dialogue is key, while climate change and co-creation with suppliers are less relevant.
Average performance is perceived in key
topics such as Customer Experience and Digital
Security.

Material issues
(GRI Content 3-2)
There were no changes in the material topics; however, they are now organized considering the three pillars of the Responsible Business Plan.

